What is intellectual property? What are the types of intellectual property rights?
Interpretation and categories of intellectual property rights
Definitions and Categories
[Intellectual property] refers to the right of citizens, legal persons or other organizations to possess, use, dispose of and benefit from their intellectual labor achievements, businesses and other specific related objects.
Simply put, it refers to the exclusive rights and exclusive rights enjoyed by creators based on intellectual achievements for a period of time. Its English name is "intellectual property", which is commonly called "IP".
The three common intellectual property rights mainly include trademark right, patent right and copyright, and trademark right and patent right are also collectively referred to as industrial property rights.
However, the scope of intellectual property rights is relatively wide, and the types classified according to relevant laws and regulations include: copyright, patent right, trademark right, geographical indication, trade secret, integrated circuit layout design, etc.
Legal basis:
Article 123 of the Civil Code of People’s Republic of China (PRC)
Civil subjects enjoy intellectual property rights according to law.
Intellectual property rights are the exclusive rights enjoyed by the obligee with respect to the following objects according to law:
(1) works;
(2) inventions, utility models and designs;
(3) Trademarks;
(4) Geographical indications;
(5) Business secrets;
(6) Layout design of integrated circuits;
(7) New plant varieties;
(8) Other objects prescribed by law.
Four characteristics of intellectual property rights
Four Characteristics
1, the intangible
Because the object of intellectual property is not tangible, but intangible works such as intellectual achievements or goodwill, goodwill or inventions, which must depend on a certain material carrier, intangible can also be called immateriality.
Generally, obtaining a material carrier does not mean enjoying the intellectual property rights it carries. In addition, the transfer of the ownership of the material carrier does not mean the transfer of the intellectual property rights it carries; Infringement of the ownership of a material carrier does not mean infringement of the intellectual property rights it carries.
For example, the published books of a writer we bought can be divided into two types of objects:
① The tangible material carrier of publishing books-the object of real right;
② The text content in published books-the object of copyright.
We acquired the ownership after purchasing the published books, but we did not acquire the copyright in the published books, so we can’t copy and distribute them privately.
2. Regionality
Intellectual property rights are only protected by law in the territory where they are legally acquired, unless there are specific provisions in international treaties, bilateral or multilateral agreements.
This is because intellectual property is not only a legal right, but also a product of a country’s public policy, which can only exist through mandatory provisions of the law, and the scope and content of the right are inextricably linked with various legal provisions of the country.
Simple understanding, such as the patent right applied in China, only takes legal effect in China; If the trademark right is registered in Japan, then the trademark right will have legal effect only in Japan.
3. Timeliness
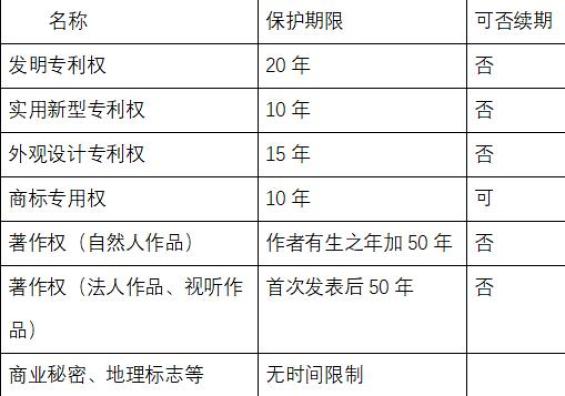
The protection period of most intellectual property rights is limited. Once the protection period stipulated by law is exceeded, the rights will automatically terminate, and related intellectual achievements will be brought into the public domain and become public resources available to everyone.
According to the relevant laws and regulations of our country, the protection period of invention patent right is 20 years; The patent protection period of design is 15 years; The protection period of utility model patent right and trademark exclusive right is 10 years, and the trademark right can be extended.
The term of protection of copyright (natural person’s works) is the author’s lifetime plus 50 years; Copyright (legal person works, audio-visual works) shall be protected for 50 years after its first publication.
There is no time limit for trade secrets and geographical indications.
4. exclusivity
Propriety means that intellectual property rights are unique to the subject of rights, and no one other than the right holder may own or use the exclusive rights of intellectual property rights without the permission of the intellectual property owner or special provisions of the law, otherwise it will constitute infringement.
The role of intellectual property rights
Function
Intellectual property, like the corresponding tangible property, has value and use value and can be traded in the market. The use of intellectual property rights mainly includes transfer, license and pledge.
Under the background of encouraging innovation in China, intellectual property strategy has become an important part of the core competitiveness of enterprises. At the same time, the establishment and implementation of intellectual property management system can also standardize enterprise management, cultivate professional and efficient teams, and prevent business risks.
How to inquire about the intellectual property rights of enterprises?
If you want to confirm the trademark, patent and other information of an enterprise, you can select the filter conditions in the [Intellectual Property] section of the enterprise general inquiry pc; You can also directly enter keywords such as "trademark name", "patent name" or "work name" in the search field. (as shown in the figure below)
Select filter query
Directly enter the trademark/patent name.
In addition, you can also check whether the information of [Website Filing] is consistent with the inquired intellectual property subject on the pc side of Enterprise Access to determine the authenticity of the subject. Because, in China, the relevant laws clearly stipulate that domestic servers cannot be used as website space without website filing.
According to the Administrative Measures for Security Protection of Computer Information Network International Networking, website filing is to prevent websites from violating laws and regulations and infringing others’ intellectual property rights.
You can directly search for keywords or filter conditions.
Legal basis:
Article 12 of the Measures for the Security Management and Protection of Computer Information Network International Networking, interconnected units, access units, legal persons and other organizations using computer information network international networking (including networking units across provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government and their affiliated branches) shall, within 30 days from the date when the network is officially connected, go through the filing formalities at the acceptance organ designated by the public security organ of the local people’s government of the province, autonomous region or municipality directly under the Central Government.
The units listed in the preceding paragraph shall be responsible for reporting the access units and users accessing this network to the local public security organ for the record, and timely reporting the changes of access units and users in this network.
Twenty-third in violation of the provisions of Article 11 and Article 12 of these measures, failing to perform the duty of filing, the public security organ shall give a warning or stop for rectification for no more than six months.
Original title: "What is intellectual property? What are the types of intellectual property rights? 》
Read the original text